The great and good are all gathered this week at Jackson Hole, sort of a Davos for powerful nerds that’s run by the Kansas City Federal Reserve. Neil Irwin reports that Robert Hall of Stanford presented an assessment of “why the housing crash and financial crisis caused such sharp and prolonged economic pain,” which prompted a 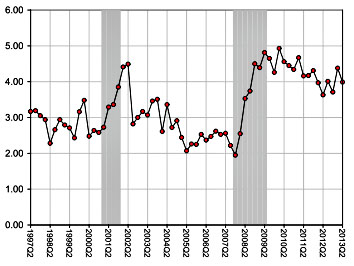 comment from Hyun Song Shin of Princeton. You may recall Shin as the ideal median economist, but in this case he’s pointing out that one big problem with the economy is that bank credit has been anemic for the past few years. As the chart on the right shows, banks normally lend at about 2.5 percentage points above the Fed’s target interest rate, but ever since 2009 they’ve been lending at about 4 points above the Fed’s target. This isn’t a huge problem for big companies, which mostly rely on bonds to finance themselves, but it is a big problem for small companies, which rely more on mortgages and bank loans.
comment from Hyun Song Shin of Princeton. You may recall Shin as the ideal median economist, but in this case he’s pointing out that one big problem with the economy is that bank credit has been anemic for the past few years. As the chart on the right shows, banks normally lend at about 2.5 percentage points above the Fed’s target interest rate, but ever since 2009 they’ve been lending at about 4 points above the Fed’s target. This isn’t a huge problem for big companies, which mostly rely on bonds to finance themselves, but it is a big problem for small companies, which rely more on mortgages and bank loans.
This reminded me of something Shin predicted a couple of years ago. During the housing bubble years, he said, European banks were indirectly providing about $5 trillion in credit to U.S. borrowers, nearly as much as American banks provided. But after the financial crisis, as European banks were forced to delever, that funding dried up. This is one way that America is suffering from Europe’s woes: Credit remains very tight, and as a result, interest rates on ordinary bank loans remain stubbornly high. Shin’s latest set of charts seem to suggest that he was right—or at least partly right—two years ago when he wrote about the malign effect of European delevering on American finance. We’re not immune just because we’re an ocean away.