Jakob Joergensen/AP
Update, 6/2/16, 10:42 a.m.: The Minneapolis Star Tribune and Associated Press report that Prince died from an opioid overdose. The autopsy and toxicology results have yet to be released publicly.
Doctors treated Prince for a drug overdose just six days before his death, TMZ reported late Thursday citing multiple unnamed sources.
The seven-time Grammy winner, best known for his eccentric personality and gifted songwriting that helped define pop music, was found unresponsive in an elevator at his Paisley Park estate and studio in Minnesota. An autopsy on Friday will help determine the exact cause of death, though information won’t be available for several days, even weeks.
News of the possible drug overdose comes during an unprecedented surge in US deaths linked to opioids, such as heroin and OxyContin. The sharp rise in overdoses has fueled a debate about making the reversal drug, which may have been used on the pop star, more widely available.
Early reports from TMZ and the Pioneer Press stated that Prince had been battling the flu for several weeks, and the pop icon told an Atlanta crowd on April 14 that he had been “a little under the weather” a week before, according to the New York Times.
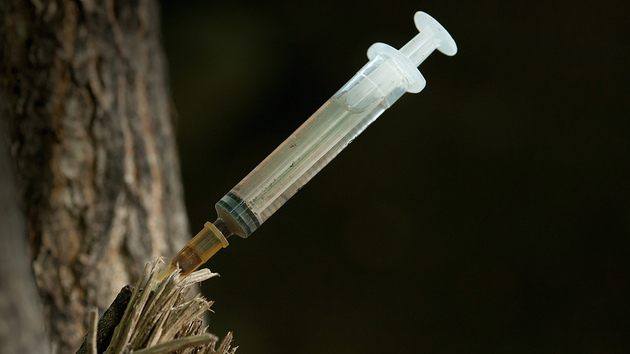
Just after 1 a.m. the following day, on his way back to Minnesota after two shows in Atlanta, the pop icon made an emergency stop at a hospital in Moline, Illinois. The celebrity news site TMZ, which first broke the news of the pop icon’s death, reported that doctors reportedly injected the 57-year-old with a “save shot” to counteract the damaging effects of an opiate overdose of Percocet, a prescription painkiller with a combination of oxycodone and acetaminophen. Prince was treated and released from the hospital three hours after his arrival.
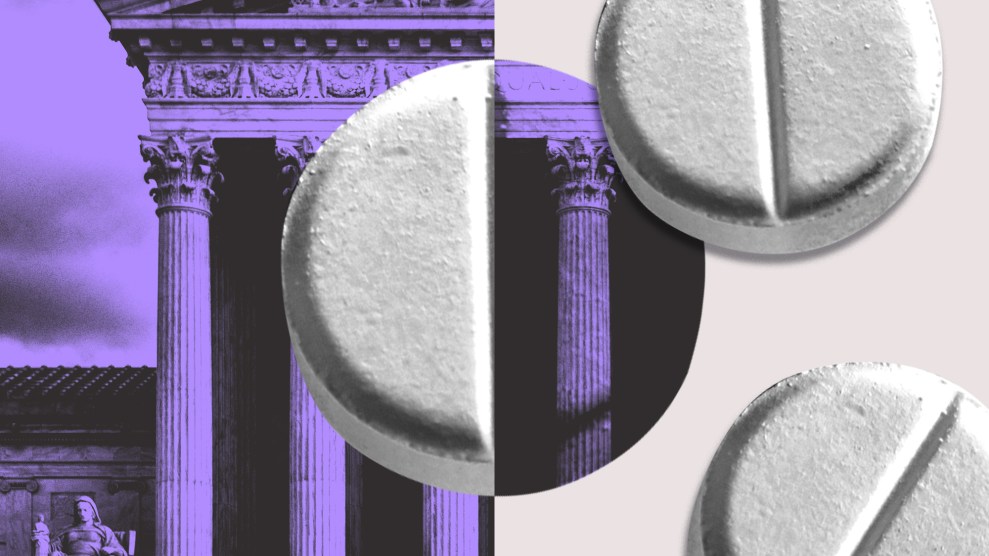
Communities across the United States are grappling with an opioid overdose epidemic. Such overdoses took more American lives than traffic accidents in 2014, and since 1999 these deaths have nearly quadrupled nationwide, with a surge particularly among young white men. The uptick in overdoses has prompted states and cities to make Naloxone, the so-called injectable “miracle drug” used in hospitals for decades, more accessible for use outside the hospital. Naloxone can save a user’s life by reversing the effects of opiates.
The Obama administration has invested $11 million toward aiding states with expanding treatment services while lawmakers and law enforcement agencies have pushed to give schools and police officers access to the reversal drug.
As my colleague Jenny Luna notes, once doctors inject the drug into the user’s system, it blocks the narcotic’s pathways to the brain and can restore normal breathing levels and consciousness if administered early enough.
You can read her story about the drug here.