Mindy Schauer/MediaNewsGroup/Orange County Register/Getty
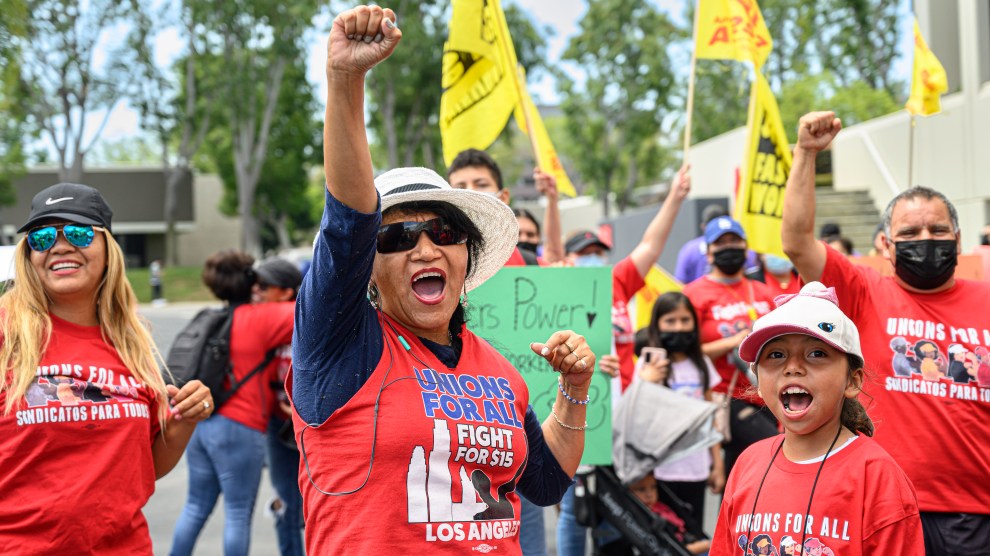
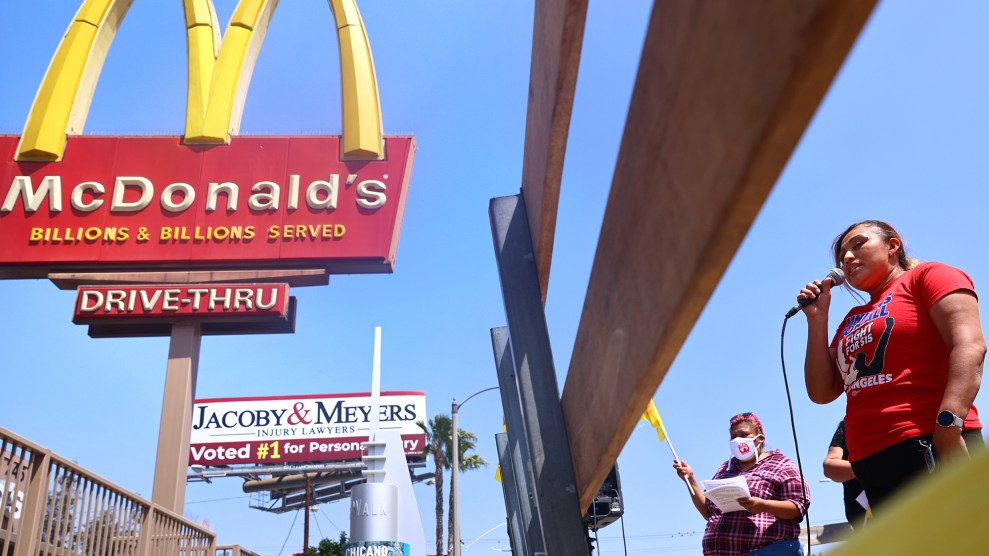
The California state legislature passed a first-of-its kind bill on Tuesday that would establish a council to set minimum wages and working conditions for the state’s more than half a million non-unionized fast food employees.
The bill, AB 257, passed the state Senate 21–12. Now, it heads to the desk of Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom, who has not announced whether he’ll sign it. The fast-food industry and the California Restaurant Association strongly oppose the bill.
As my colleague Noah Lanard wrote earlier this month:
AB 257 resembles what is known as “sectoral bargaining,” a process by which workers negotiate collective bargaining agreements that apply to entire industries. The practice has been used to great effect in countries like Germany and Denmark, but it is not permitted under American labor law. Instead, workers here must negotiate contracts that cover individual companies, or parts of companies such as an individual store or warehouse.
The California bill would establish…a council composed of fast-food workers and their advocates, industry representatives, and state officials. Together, they would be responsible for determining minimum wages, along with hours and working conditions, across California’s fast-food industry.
The Senate vote came after intense negotiations in which the bill’s critics managed to eliminate provisions that would allow the council to establish sick-leave or paid-time-off benefits. Joint liability, which would force franchisors to hold some responsibility for conditions at individual store locations, was also axed.
Still, if the bill becomes law, it will be a major victory for a labor movement that has struggled to notch legislative wins at the national level.