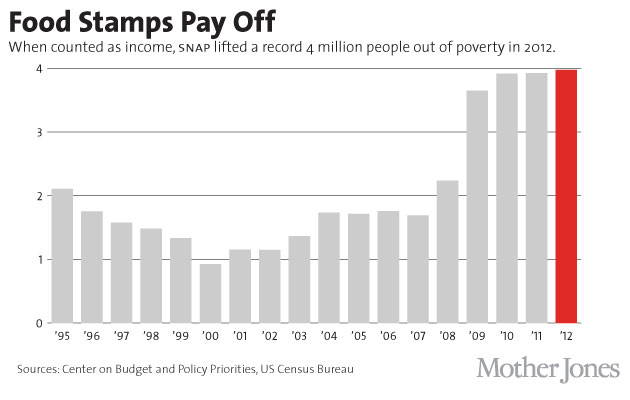
In September, just two days after a Census Bureau report showed that food stamps helped keep 4 million Americans out of poverty last year, the US House of Representatives approved a $39 billion cut to the program (known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, or SNAP) over the next decade.
The House proposal, now being negotiated along with smaller, yet still significant, Senate cuts of $4 billion, would result in 3.8 million people being removed from food stamps in 2014, according to the Congressional Budget Office. The haggling comes at a time when more than 15 percent of Americans remain mired in poverty, and more than half are at or near the poverty line when stagnant middle-class wages are matched against rising costs of living, US Census data show.
Although the Republican-controlled House cuts are unlikely, given a promised veto from President Obama, food stamps will still be slashed by $5 billion on Nov. 1, when the 2009 Recovery Act that increased the aid along with other stimulus spending expires. The 13.6 percent temporary boost in food stamp dollars helped more than half a million Americans escape food insecurity, and millions more to climb out of poverty—4.7 million in 2011 alone, according the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities (CBPP).
Eighty-three percent of food stamps go to households with children, seniors, and nonelderly people with disabilities. The Nov. 1 reduction means $36 less per month for a family of four and $11 less for a single person. In 2012, the average recipient got $133.41 in food stamps per month—that works out to $1.48 per meal. “Without the Recovery Act’s boost, SNAP benefits will average less than $1.40 per person per meal in 2014,” reports the CBPP.
“The Republican attack on food stamps is “totally counter-factual,” says Peter Edelman, a professor of law at Georgetown University and a former Clinton administration official who resigned in protest of the 1996 welfare overhaul. “Millions of people are unemployed and millions more don’t earn enough to pay all their bills. The idea that food stamps, which provide support at one-third of the poverty line, is incentivizing people not to seek jobs that don’t exist anyway is beyond bizarre.”
Extensive research shows food stamps are a highly effective investment delivering big returns for all Americans, not just the poor. SNAP not only provides an economic and nutritional lifeline for low-income Americans, it also creates a significant boon to the wider economy.
The Economic Benefits of Food Stamps
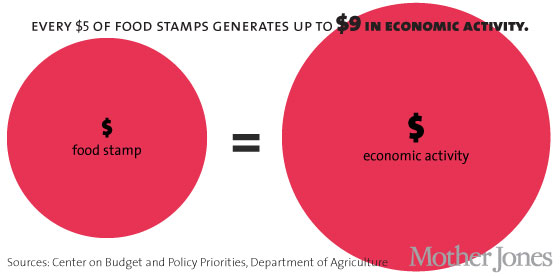
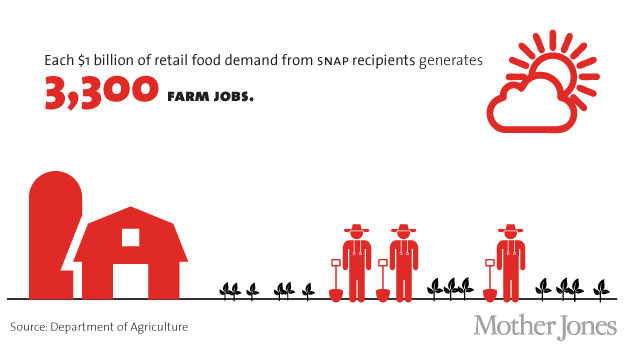
When food stamps get spent, we all benefit. Despite critics’ focus on the costs of SNAP, research has shown that these dollars are among the best forms of government stimulus. Food stamp spending generates local economic activity, jobs in the farm and retail sectors and beyond.
Food Stamps Lift Millions Out of Poverty
In addition to boosting the economy and job creation, food stamps have helped millions of Americans climb out of poverty and away from hunger. The dollars put food on the table, and by covering much of poor people’s food expenses, free up vitally needed cash to cover rent and other necessities. That can help people stabilize their lives and get back on their feet. Since SNAP expanded in 2009, according to the USDA, “food insecurity among likely SNAP-eligible households declined by 2.2 percent, and very low food security declined by 2 percent; food spending rose by 4.8 percent.”
Food Stamps Improve Kids’ Health
Children are especially vulnerable to the lifelong ripple effects of poverty—exposed to hunger, under-nourishment, and a greater likelihood of chronic illnesses and disease. But studies show that when poor families get food stamps, kids’ nutrition and health improve. This can be particularly critical during infancy and early childhood, when brain development and metabolic health get their start. The added food and nutrition from food stamps has been shown to create marked health improvements both in childhood and later years.


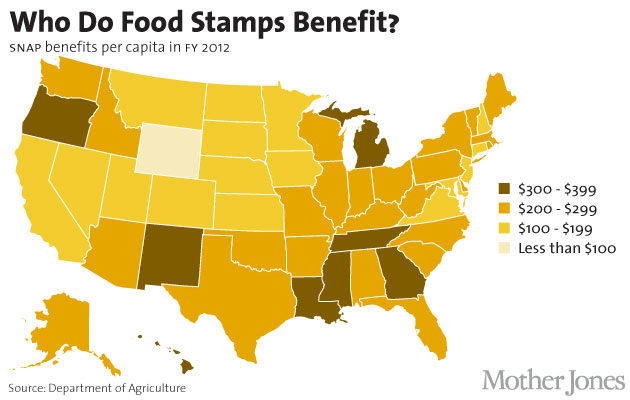
Who Gets Food Stamps?
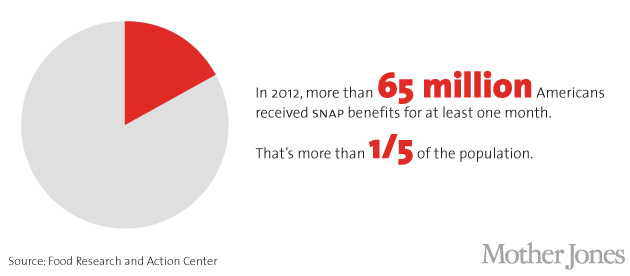
An extraordinary number of Americans have benefited or will benefit directly from food stamps. Half of all adults (pdf) will receive SNAP benefits at some point between the ages of 20 and 65, while half of all children will receive them at some point during their childhood. In 2012, nearly 1 in 7 adults received food stamps.
This article was produced in collaboration with the Food & Environment Reporting Network, an independent, non-profit news organization producing investigative reporting on food, agriculture and environmental health.