<a href="http://www.istockphoto.com/photo/bacteria-green-7371965?st=d406054"> fpm</a>/iStock
In 1945, Sir Alexander Fleming won a Nobel Prize for his discovery of penicillin, which transformed modern medicine. Later that year, the bacteriologist issued a prescient warning: The miracle medicine could one day come with dangerous side effects. If antibiotics were overused, he told the New York Times, bacteria would develop resistance and spur a new generation of bugs impervious to the drugs’ power.
In the last 60 years, Fleming’s advice has gone largely unheeded. Antibiotic consumption continues to grow even as health officials around the world sound the alarm over rising numbers of resistant bacteria. Now, a new report from the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy (CDDEP), a multidisciplinary research organization, paints a harrowing picture of where we stand in the arms race against antibiotic resistance. The main finding is grim: Antibiotic consumption rose by 30 percent between 2000 and 2010 and is expected to swell further as demand for drugs and mass-produced meat products grow around the world.
“Antibiotic resistance is now clearly a problem in both the developed world and developing countries,” coauthor Ramanan Laxminarayan told National Geographic. “Things are about to get a lot worse before they get better.”
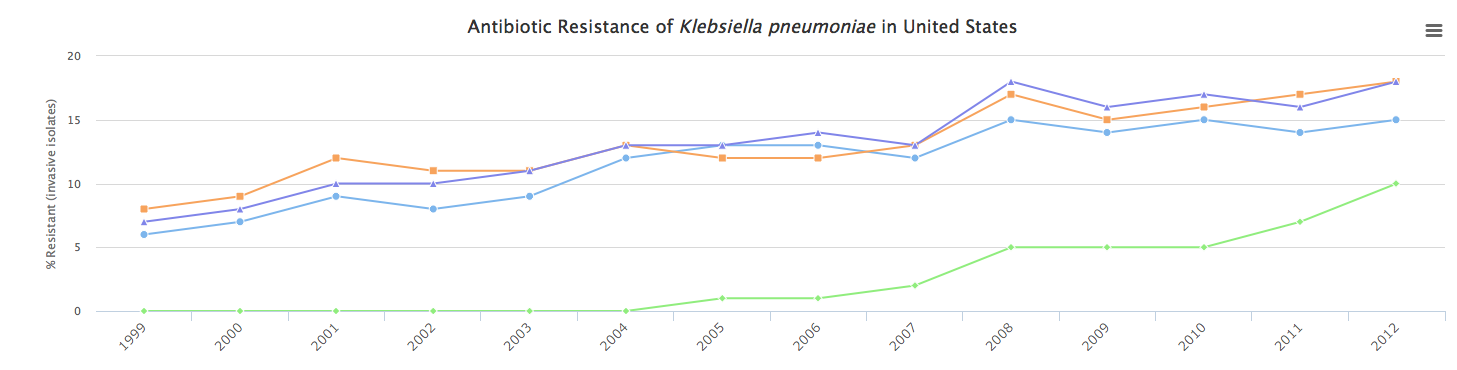
With the report, CDDEP also launched an interactive data visualization that shows antibiotic use from 69 countries. Additional charts also show antibiotic resistance rates of 12 different types of bacteria. For example:
One reason for the rising rates of resistance: Many developing countries that now have access to affordable antibiotics do not yet have the infrastructure to regulate them. The report highlights that 80 percent of antibiotics are consumed in communities and not in hospitals, and are often not prescribed by doctors. Many of the drugs being used are intended only for emergency cases. As Maryn McKenna reported in National Geographic:
Troublingly, that rising consumption worldwide takes in the most precious last-ditch drugs. Carbapenem use rose by 40 percent between 2000 and 2010, and the use of the very last-resort drug class polymixins rose by 13 percent. Sales of those drugs are rising fastest in India, Pakistan and Egypt, and many of those sales are retail, outside countries’ healthcare systems.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, of the roughly 2 million people in the United States afflicted every year with illnesses caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, 23,000 of them will die. These illnesses cost around $20 billion each year, and lead to an additional $35 billion in productivity losses.
In response to the imminent and growing threat of antibiotic resistance, this year, the White House launched the National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria, which aims to cut down on overuse in the next five years. While it does offer a promising framework for better practices in health care, as my colleague Tom Phillpot reports, regulations fall short in one of the key areas of antibiotic overuse: agriculture. The meat industry consumes an unbelievable 80 percent of all antibiotics sold in the United States.
The Food and Drug Administration’s voluntary guidelines advise against the use of antibiotics for animal growth—but the industry continues to exploit regulatory loopholes and administer growing amounts of antibiotics to the animals we eat.
Worldwide, according to the report, more than 63,000 tons of antibiotics were given to livestock in 2010, and this number is only expected to grow. Over the next 15 years, as demand for meat grows around the world and small scale farms switch to mass production to keep up, animal consumption of antibiotics is projected to increase by 67 percent.
While the outlook on growing antibiotic use and the likelihood of increased resistance seems grim, the authors of the report offer six strategies that could help curb the issues before they get worse:
- Reduce the need for antibiotics through improved water, sanitation, and immunization
- Improve hospital infection control and antibiotic stewardship
- Change incentives that encourage antibiotic overuse and misuse to incentives that encourage antibiotic stewardship
- Reduce and eventually phase out subtherapuetic antibiotic use in agriculture
- Educate and inform health professionals, policymakers, and the public on sustainable antibiotic use
- Ensure political commitment to meet the threat of antibiotic resistance
Earlier this year, the World Health Organizations’ governing body, the World Health Assembly, called for its member countries to adopt policies that will curb antibiotic use by 2017. The report’s authors hope their findings will lead to stronger stewardship around the world.
“With support from WHO and the international community, this resolution could catalyze change—or, like similar resolutions over the past decade, it may be ignored,” they write. “The evidence in this report, documenting the seriousness of the problem and offering a successful approach to country level action, supports both the urgency and the feasibility of making progress in conserving antibiotic effectiveness.”