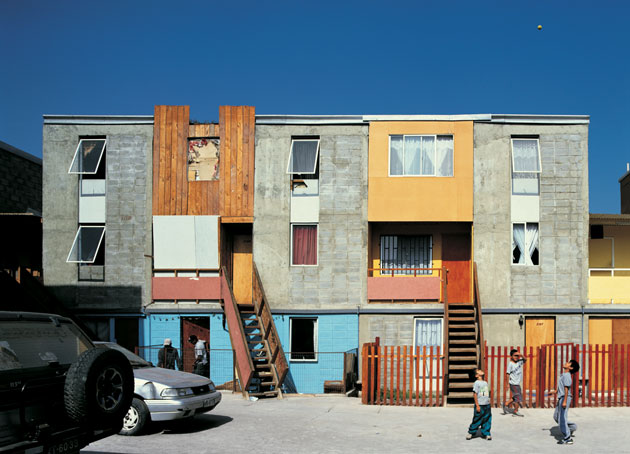
The Quinta Monroy houses in Chile. Residents start with the gray, concrete structure and foundations, then fill in the adjacent spaces with their own materials over time. Cristóbal Palma/Verso Books

In the United States, we tend to think of the suburbs as the historic domain of the middle class. It’s where the boomers went after fleeing the cities to accommodate their growing families (although the demographics of the suburbs are now changing).
But in Latin America, urban peripheries are less commonly populated by leafy suburbs for the rich than by slums for the poor. These shantytowns typically lack basic infrastructure like paved roads, sewers, and tap water. Living far from the city, residents are often forced to make long and expensive commutes.
But in the medium-sized Chilean port city of Iquique, one architect, Alejandro Aravena, had a solution: partial houses, located at the center of town, equipped with only the barest necessities—and space for residents to build on, bit by bit, as they can afford it.
When they were first built fourteen years ago for about 100 families, Aravena’s flagship projects, called the Quinta Monroy Houses, came with all the core necessities—a roof, a bathroom, a kitchen. With a little more than 300 square feet in floor space to start with, the houses were 25 percent smaller than the average public housing unit in Chile, but with an extra-wide foundation, residents had plenty of room to expand.
In his new book, Radical Cities: Across Latin America in Search of a New Architecture, journalist Justin McGuirk writes that when Aravena first launched the project through his firm, Elemental, a number of critics were appalled. They argued that the government should provide complete houses, since incomplete houses require the occupant to perform manual labor. But where some saw a failure in the making, others welcomed change. In the 1970’s, under Chile’s socialist president Salvador Allende, the government prioritized building completed public housing, even enlisting a Soviet-made pre-fabricated house factory for the job. But despite the initial gusto, the government quickly ran out of the resources to continue. In three years, the slum population rose more than 130 percent.
Since the Allende period, the government has shifted to a hybrid market-government approach, giving subsidies to the poor to buy houses and land. At the time Aravena built Quinta Monroy, the government offered $7,500 per family—usually too little to buy a complete house, but just enough to make Aravena’s stripped-down models affordable.
As residents expanded their houses, their value grew. One study (PDF), sponsored by the Finnish government, found that in its first two years, Quinta Monroy’s 100 families had made an average of $750 in improvements per unit, doubling the size of their homes and raising the houses’ value to an estimated $20,000 each. One six-year resident McGuirk speaks with says that after the subsidy, he spent just $400 of his own money to buy a basic Quinta Monroy house. But after saving up and adding four bedrooms and an extra bathroom, he estimates he has increased the value of his home to $50,000.
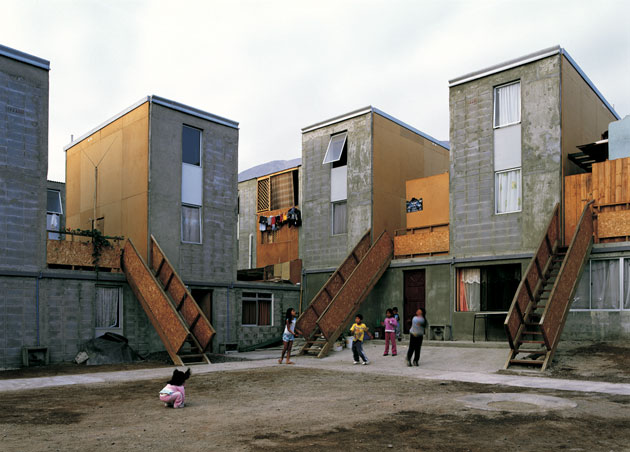

It’s hard to see a plan like this taking off in the United States, given our long permitting processes and strict building codes. And even in Iquique, some of the half-houses look similar to the shantytowns they were designed to replace: While some residents have transformed their homes into elegant structures with balconies and trim, “other add-ons look like slum shacks wedged between concrete houses,” McGuirk says.
Still, other countries see promise in Aravena’s idea. Already, Elemental has built and sold hundreds of half-houses in Chile, and it’s testing the idea in Mexico, Guatemala, and Peru. “These are places where Aravena can still make a difference,” McGuirk says.