In an updated study released Thursday, the Sentencing Project reports that close to 6 million Americans are now unable to vote thanks to felon disenfranchisement laws. “Approximately 2.5 percent of the total US voting age population—1 of every 40 adults—is disenfranchised due to a current or previous felony conviction,” notes the report, authored by Christopher Uggen and Sarah Shannon of the University of Minnesota and Jeff Manza of New York University.
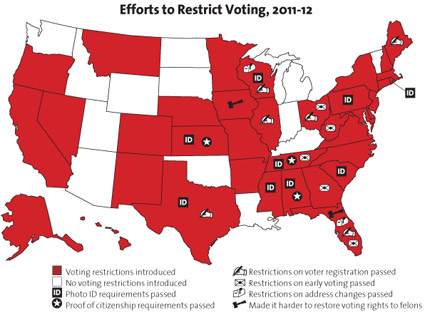
The numbers have risen dramatically over the decades, due both to the rise of mass incarceration in the United States and to the spread of restrictive state voting laws. As we reported last week, nearly all states bar imprisoned felons from voting, 29 states bar them even after they have served their time, and a handful—including several battleground states—effectively bar them for life. The number of affected Americans has ballooned from 1.2 million people in 1976 to 3.3 million in 1996. As of 2010, the figure stands at 5.9 million.
Rates of disenfranchisement vary dramatically by state due to broad variations in voting prohibitions. In six states—Alabama, Florida, Kentucky, Mississippi, Tennessee, and Virginia—more than 7 percent of the adult population is disenfranchised.
In what amounts to a modern-day version of Jim Crow-era statutes, felon disenfranchisement takes a substantial bite out of the black vote. According to the report, nearly 8 percent of voting-age black Americans (1 in 13) is disenfranchised, compared with roughly 2 percent of their non-black counterparts. In three states—Florida, Kentucky, and Virginia, at least 1 in 5 black Americans will be out of luck come Election Day. In the cases of Florida and Virginia, the numbers are sizeable enough to change the outcome in November. As Desmond Meade of the nonprofit Florida Rights Restoration Coalition put it to us last week: If these people were able to vote, “Florida would no longer be a swing state.”