John Minchillo/AP
President Barack Obama announced a new federal initiative to combat the country’s painkiller problem ahead of a speech on Wednesday in Charleston, West Virginia, a place at the heart of an opiate crisis. In greater Kanawha County, of the 65 people who have died from drug overdoses so far this year, 22 people have succumbed to heroin. The same number of people have died from heroin in nearby Cabell County, the epicenter of the state’s drug problem.
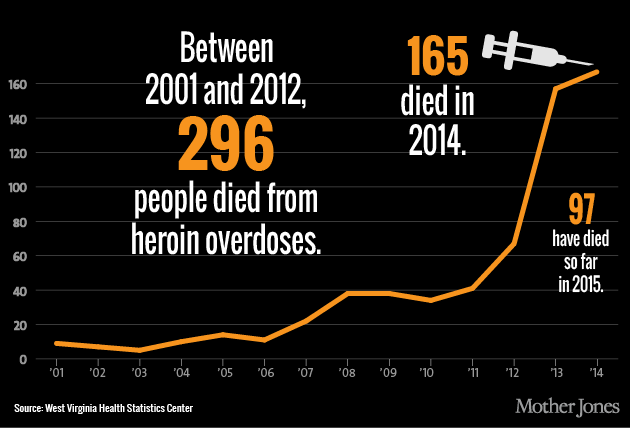
For the last half decade, the state has been gripped by the rise of prescription opiates and heroin, just as the rest of the country has encountered the revival of the cheap painkiller as a drug of choice. In 36 states and the District of Columbia, deaths from drug overdoses have outnumbered those from auto accidents, with West Virginia leading the way. Of the 363 drug overdoses in West Virginia so far this year, roughly 88 percent were opiate-related and included multiple substances, with 97 deaths related to heroin overdoses, according to new data from the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources’ Health Statistics Center.
A crackdown on cash-only clinics for prescription painkillers and a flood of pure heroin from nearby cities have contributed to West Virginia’s drug problem. But just how bad is it?