Containers at Shenzhen Port in China, one of the busiest in the world. Liu Xianglong/Imaginechina/ZUMA
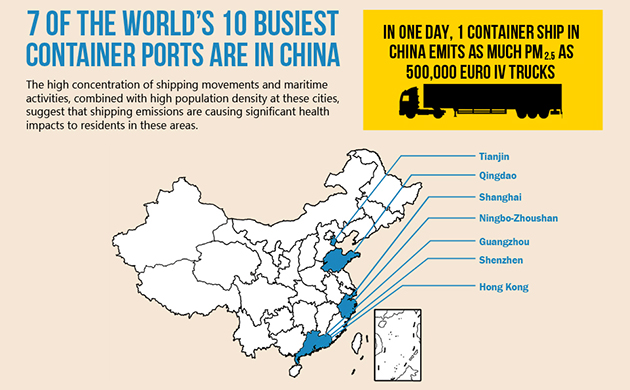
If you’ve recently purchased a new iPhone, or a fancy t-shirt, or a children’s toy… or really virtually any consumer or industrial good, there’s a strong chance that a giant ship ferried it from or through China. China, dubbed “the world’s factory” for pumping out so much of the world’s consumables, now boasts seven of the world’s top ten busiest trading ports. Strung up and down its densely populated eastern coast, China’s ten biggest ports handle nearly 30 percent of the world’s containers each year.
These mega-ports—Shanghai’s is the planet’s busiest—helped China become the biggest trader in the world, eclipsing the US in 2012. China has also become the world’s second largest consumer market—meaning that more and more ships are unloading wares in the country’s ports, not just loading up.
But there’s a big downside for the planet in all that trade, according to a report released Tuesday by the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), a US-based environmental advocacy group with offices in Beijing. When the country’s brutal smog and worsening air crisis make international headlines, as it did earlier this month after runners in the Beijing marathon donned air masks, coal burning and China’s grid-locked streets get most of the attention. But emissions from China’s vast shipping industry have so far been “very much overlooked” by Chinese leaders, says Barbara Finamore, an author of the report and NRDC’s Asia director.
“Last September, the central government issued a national air control plan and it only mentioned this in passing,” she said in a phone interview from Beijing.
Finamore’s report argues that poor regulation in China means that in a single day one container ship can pollute as much as half a million trucks:
That’s because regulations allow China’s oceangoing ships to burn fuel with sulfur levels that are 100 to 3,500 times higher than those permitted for road vehicles, according to the report. This so-called “bunker oil” is extremely dirty and spews toxic exhaust into the air, including harmful diesel particulates, and nitrogen oxide and sulfur oxide that cause smog. Those chemicals are known to lead to respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses. Shipping is not a small contributor: Two thirds of the sulfur pollution in the Chinese megacity of Shenzhen, near Hong Kong, comes from the shipping industry, says Finamore.
The exhaust not only pollutes the air locally, but also carries a powerful climate toll: A portion of the exhaust is “black carbon,” a fine particulate that, after CO2, is the second largest contributor to global warming. The US Environmental Protection Agency says it is particularly potent in melting arctic sea ice. As more ships take polar routes made more hospitable by warming, the black carbon they leave behind may accelerate melting, potentially further opening up once ice-bound lanes for more shipping. “It’s a vicious cycle,” says Finamore.
The report finds that 70 percent of emissions from major shipping routes occur within 400 km (about 250 miles) of a coastline, and that emissions can travel hundreds of miles inland. Stricter rules in North America (especially in California) and Europe mandate cleaner fuel when coming into port, and China is working to implement similar standards. In July, Hong Kong became the first city in China to regulate shipping emissions; other Chinese port cities and coastal regions have begun to introduce other control measures.
What works? According to the NRDC, there are three areas that could help clean up the industry, including moving to natural gas, using cleaner fuels, and powering down ships in ports:

In a country where ambient air pollution contributed to an estimated 1.2 million premature deaths in 2010, Finamore says leaders are “scrambling” for solutions.
It’s this kind of pollution—and the public discontent it causes—that has gotten attention from the highest levels of government. Vice Premier Li Keqiang, the second-ranking Chinese official, formally declared a “war on pollution” earlier this year. Another Chinese leader gave a speech at the September UN climate talks in New York pledging that China would reach a peak in emissions “as soon as possible”—an unprecedented promise.
“They are taking it seriously,” Finamore says. “They are doing more than ever before to examine the environmental issues of various plans and sources of energy.”
But in China, she says, “implementation is always a problem.”