Here’s an interesting thing. Using data from Missouri, a team of researchers looked into what happens when cities face a revenue squeeze. As you’ve always expected, one thing that happens is that cops write more tickets. Interestingly, though, they found that citation rates of Black and Latino drivers stayed about the same. It was only the citation rate of white drivers that went up:
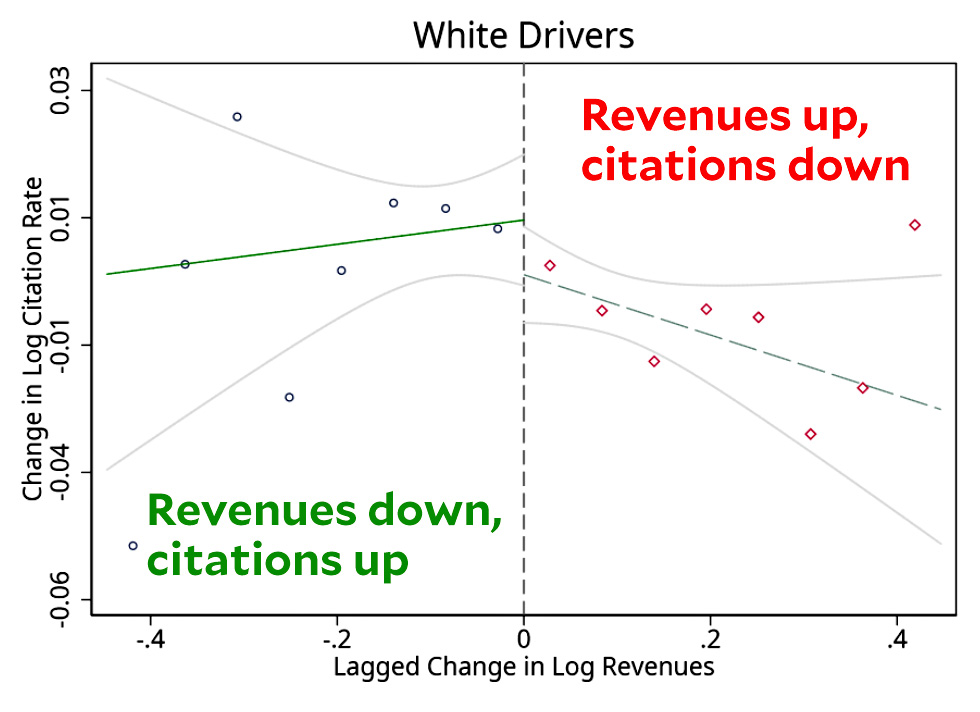
This is interesting, but I think the authors’ interpretation is backward. In fact, the citation rate of white drivers barely changes at the zero point. What’s more noteworthy is that when times are flush (right side of chart) and police can afford to ease up, they ease up on white drivers but not Black or Latino drivers. (The full set of charts is here on p. 25.)
That’s my take, anyway. The authors suggest that when times are tough, cops focus on white drivers because they’re more likely to be affluent and therefore more likely to actually pay their fines. That may be. But when I look at this data without the distracting discontinuity overlay…
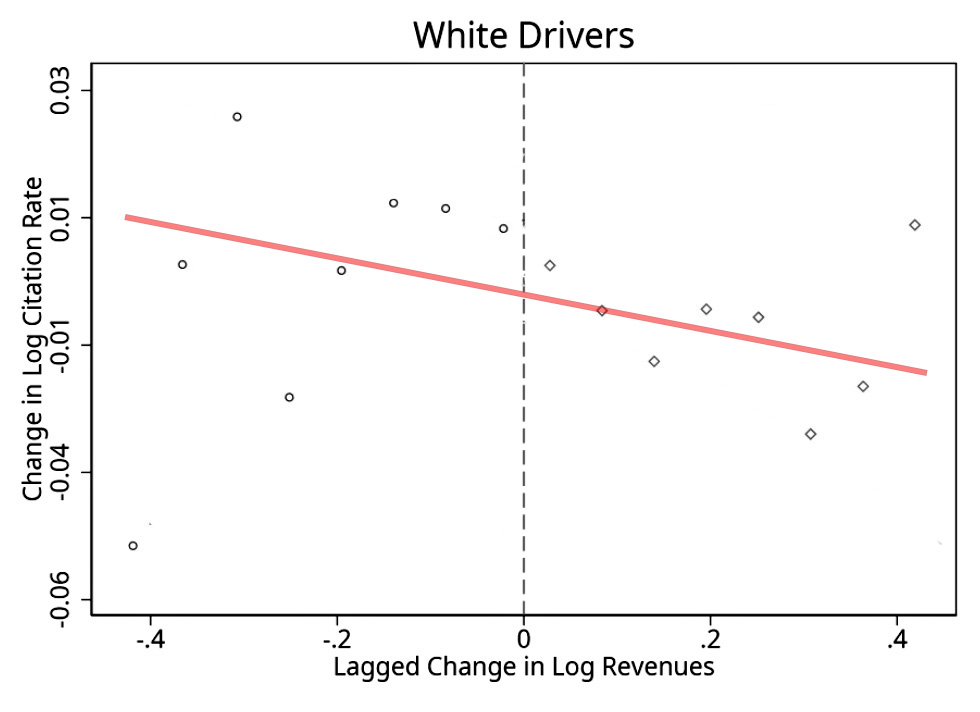
What I mostly see is a fairly simple story where there’s one weird outlier (bottom left) and the most obvious overall interpretation is that white drivers benefit from improved municipal revenue across the board, with nothing special happening at the zero point. The better things are, the more that white drivers are let off the hook. But only white drivers.
Of course, this whole thing would be moot if traffic fines weren’t used as revenue generators in the first place. “Policiteering,” as Jack Hitt dubbed it five years ago, was one of the key features of life in Ferguson, Missouri, before Michael Brown was shot and killed:
In 2010, this collaboration between the Ferguson police and the courts generated $1.4 million in income for the city. This year, they will more than double that amount—$3.1 million—providing nearly a quarter of the city’s $13 million budget, almost all of it extracted from its poorest African American citizens.
Is there any tax on the planet more regressive than this? It needs to end.