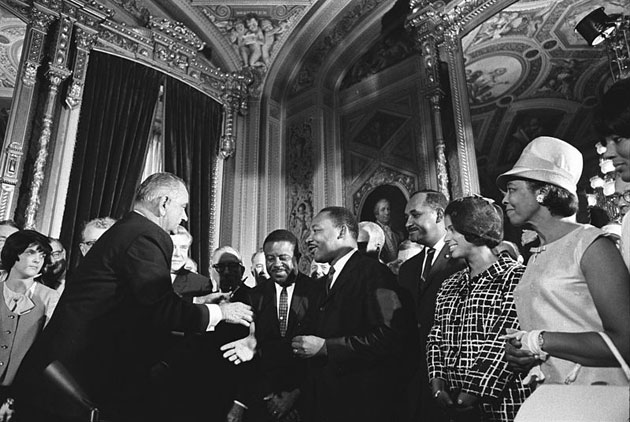
President Johnson, Martin Luther King, Jr. and Rosa Parks at the signing of the Voting Rights Act on August 6, 1965.<a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lyndon_Johnson_and_Martin_Luther_King,_Jr._-_Voting_Rights_Act.jpg">Wikimedia Commons</a>
A key pillar of American civil rights law is now in danger of being nullified by the Supreme Court.
Shelby County, Alabama, is seeking to have Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act, the law that first guaranteed the right of blacks in the South to vote, declared unconstitutional. Section 5 forces areas of the country with a history of discrimination—mostly, but not entirely in the South—to ask the Department of Justice for its approval before making any changes to election rules. The DOJ is then supposed to ensure any changes protect Americans’ voting rights. The law has a provision allowing jurisdictions to “bail out,” but conservatives have repeatedly challeged the law as unconstitutional federal overreach that is no longer necessary because America has transcended its history of racial discrimination. The Supreme Court announced Friday that it would take up the case.
The last time conservatives challenged Section 5, in 2009, the Supreme Court handed down a very narrow 8-1 ruling (Clarence Thomas was the only dissenter) that did not declare the law unconstitutional.
The fact that the court is taking up a Section 5 case again so soon suggests strongly that the intent is to strike down part or all of the Voting Rights Act.
Although Section 5 survived in 2009, conservative justices appeared to believe that the law was discriminatory—against Southern white people. “Is it your position that today Southerners are more likely to discriminate than Northerners?” Chief Justice John Roberts demanded of the attorney defending the Voting Rights Act at the time. Despite the 8-1 vote, the 2009 decision was widely seen as leaving Section 5 hanging by a thread. The justices hinted very strongly that Congress, which had just reauthorized the Voting Rights Act in its entirety in 2006, should change the law soon or risk it being declared unconstitutional next time around.
Now it looks like the conservatives on the court will get their chance. A cursory review of recent Republican shenanigans with voting rules should put the notion that the VRA is obsolete entirely to bed. With voting growing more racially polarized, the temptations to alter voting rules to disenfranchise particular constituencies is obvious. Indeed, the Department of Justice successfully challenged Texas’ redistricting map because it diluted the voting power of Latinos. If the court strikes Section 5 down, one of the most effective and important powers the federal government has for ensuring that the right to vote is not abridged on the basis of race will be destroyed.