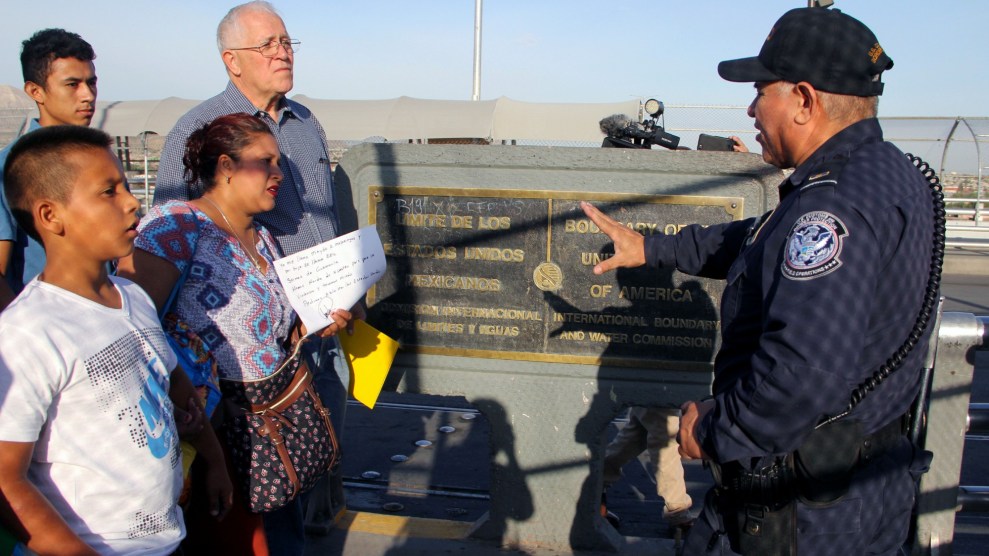
A Customs and Border Protection Agent talks to a US activist.Herika Martinez/AFP/Getty
This story was published originally by ProPublica, a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up for ProPublica’s Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this in your inbox as soon as they are published.
Taylor Levy couldn’t understand why she’d been held for hours by Customs and Border Protection officials when crossing back into El Paso, Texas, after getting dinner with friends in Ciudad Juarez, Mexico, in January 2019. And she didn’t know why she was being questioned by an agent who’d introduced himself as a counterterrorism specialist.
Levy was part of the legal team representing the father of a girl who’d died the previous month in the custody of the Border Patrol, which is part of CBP. “There was so much hate for immigration lawyers at that time,” she recalled. “I thought that somebody had put in an anonymous tip that I was a terrorist.”
The truth was more troubling. Newly released records show that Levy was swept up as part of a broader than previously known push by the administration of President Donald Trump to use the federal government’s expansive powers at the border to stop and question journalists, lawyers and activists.
The records reveal that Levy and attorney Héctor Ruiz were interrogated by members of CBP’s secretive Tactical Terrorism Response Team. The lawyers were suspected of “providing assistance” to the migrant caravan that was then the focus of significant attention by the administration and right-wing media. Officials speculated in later reports that immigration lawyers were seeking to profit by moving migrants through Mexico, and that “Antifa” may have been involved.
The records were provided to ProPublica by the Santa Fe Dreamers Project, a public interest law firm and advocacy group that received them after filing a Freedom of Information Act lawsuit about the stops of Levy and Ruiz at the border in El Paso.
Following revelations two years ago by NBC 7 San Diego that some journalists and others were targeted for questioning when crossing from Tijuana, Mexico, the Trump administration maintained that the incidents were limited to San Diego and a handful of U.S. citizens. But the new documents prove the operation went further—and raise questions about how many others were targeted.
While the records are heavily redacted, they provide a window into exactly how the targeting worked. They also show that the push was based in part on claims that were simply wrong—for example, that Levy met with members of the caravan in Mexico while they were traveling towards the border.
“This whole thing is COINTELPRO for dummies,” said Mohammad Tajsar, an attorney at the American Civil Liberties Union, referring to a notorious domestic spying program from decades ago. Tajsar is representing some of the San Diego activists who were stopped. An “intel-gathering apparatus was shared and deployed through a number of different agencies and resulted in a dragnet that ensnared a whole bunch of people.”
Responding to questions from ProPublica, a CBP spokesperson said in a statement: “In response to incidents in November 2018 and January 2019, which included assaults against Border Patrol Agents, CBP identified individuals who may have information relating to the instigators and/or organizers of these attacks. Efforts to gather this type of information are a standard law enforcement practice.” The statement does not address the targeting of Levy and Ruiz or what role investigators suspected two lawyers in El Paso of playing in attacks on federal agents that were in San Diego.
The administration of President Joe Biden is continuing to fight several lawsuits filed against the Trump administration over the operation. The Department of Homeland Security’s inspector general promised to investigate the allegations in 2019, as the CBP spokesperson noted to ProPublica, but it has not published its findings. The current head of U.S. Border Patrol is a career agent who was in charge of the San Diego sector when agents there were helping lead the surveillance effort.
Neither Levy nor Ruiz were told why they were being questioned. What they were asked about didn’t give them many clues. Both were questioned about their activities in Mexico — specifically, if they had been to Tijuana recently. They were questioned about their jobs and educational backgrounds; Ruiz was asked about the funding of the Santa Fe Dreamers Project, where they work as an attorney.
Both lawyers also recall being asked about their beliefs. Levy remembers an agent asking her why she worked for a Catholic aid organization if she didn’t believe in God, while Ruiz told ProPublica they were asked about their opinions of the Trump administration and the economy. Government notes of their interviews provided as part of the suit don’t reference those questions, but they do cite comments from both Levy and Ruiz criticizing Trump’s border policies.
Ruiz ultimately agreed to a phone search, despite their concerns about agents reading privileged attorney-client communications, which is exactly what the agents did. The records note the use of WhatsApp to communicate with people described as “foreign national”—Ruiz’s clients.
Ruiz didn’t tell anyone about their late-night interrogation for weeks after it happened. When they learned the same thing had happened to Levy, and when the NBC 7 story appeared two months later showing that similar episodes in San Diego had been part of a deliberate targeting effort, the El Paso lawyers sought to find out if they had been on the same watchlist. So Ruiz’s then-colleague Allegra Love filed a Freedom of Information Act request followed by a lawsuit.
This spring, they finally got a complete-enough set of documents to piece the truth together.
In late November 2018, writing up an interview with a migrant who’d traveled with the “caravan,” San Diego-area border agents identified Levy and Ruiz as two of “three attorneys/legal assistants that most likely traveled to meet with the caravan.” The redacted notes leave it unclear whether the migrant identified the two by name, or whether agents made the connection on their own. Either way, by the time that email was forwarded to San Diego’s Border Intelligence Center, the two were identified as “ASSOCIATED TO THE MIGRANT CARAVAN DEC 2018.”
In fact, Levy had not only never met with people in the caravan, colleagues recall she’d vocally criticized the caravan at the time. Ruiz had conducted some legal workshops for caravan migrants weeks before their arrival in Tijuana, when they’d been staying in a soccer stadium in Mexico City. Ruiz and Love told ProPublica they had encouraged migrants with tenuous asylum claims not to attempt to come to the U.S. and didn’t have any further involvement with the group.
According to emails obtained in the lawsuit, agents were instructed to flag Levy and Ruiz (as well as three others whose information is redacted) in the system for screening people coming through U.S. ports of entry.
When Ruiz came back to El Paso after a night out in Ciudad Juarez in December, and when Levy returned from that January dinner, the port officer checking their passports saw an alert that they should be interrogated by a member of CBP’s Tactical Terrorism Response Team.
The team’s stated mission is to stop suspected foreign terrorists from entering the country. But the government has expanded powers at the border that allow it to stop and question civilians entering the U.S. Records produced in an ongoing ACLU Freedom of Information Act lawsuit about the unit have shown that its members frequently question American citizens. (CBP did not respond to questions about the role of the terrorism teams.)
What exactly the interrogations of Levy and Ruiz were trying to uncover still isn’t clear. Levy and Ruiz both got the impression that they were being accused of “coaching” asylum-seekers to lie to border agents. The newly disclosed records don’t include anything about that, at least not in the unredacted text, but they do say that Ruiz “admitted to facilitating the migrant caravan by providing legal guidance free of charge and educate the migrant’s with the Asylum process.”
The accusation that telling asylum-seekers about how U.S. law works is “facilitating” their entry reflected a broader suspicion that asylum-seekers were trying to subvert U.S. law rather than accessing a legal right. One Border Patrol email from the San Diego side of the targeting operation, obtained in a Freedom of Information Act lawsuit by NBC 7 and the Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press and shared with ProPublica, referred to crossing the border to claim asylum as exploiting “a loophole.”
A Border Patrol intelligence report from El Paso, written several months after Levy and Ruiz were interrogated and included in the newly released documents, cast further aspersions on asylum lawyers. The report states, “Mass migration from South America into the United States is said to be coordinated at some level by non profit organizations who wish to line their pockets with proceeds deriving from migrants transportation fees up to the U.S Mexico border, and ultimately proceeds deriving from the migrants paying for their asylum case lawyers once they have arrived to the United States.” It goes on to associate this effort with “other groups such as Antifa.”
The report also asserts, inaccurately, that Levy and Ruiz were “seen in Tijuana assisting with the migrant caravan.”
Now that the lawyers know more about why they were stopped—and by whom—they are all the more concerned it could happen again. Levy has since moved to California but told ProPublica she fears retaliation for this article.
Ruiz still crosses the border multiple times a week for work. “I’m still super fearful,” they told ProPublica. “I don’t know if this is the day they’re going to detain me again.” The caravans and Trump are both gone, but “I’m still doing this work. And I don’t know what sort of false accusations they can throw going forward.”