<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/cat.mhtml?lang=en&language=en&ref_site=photo&search_source=search_form&version=llv1&anyorall=all&safesearch=1&use_local_boost=1&autocomplete_id=&searchterm=hiv%20test&show_color_wheel=1&orient=&commercial_ok=&media_type=images&search_cat=&searchtermx=&photographer_name=&people_gender=&people_age=&people_ethnicity=&people_number=&color=&page=1&inline=103536578">science photo</a>/Shutterstock
On the surface, the news about HIV in the United States sounds good. According to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the diagnosis rate dropped 19 percent from 2005 to 2014—a dramatic decline. Among heterosexuals, new HIV diagnoses fell by 35 percent; among people who inject drugs, 63 percent; among women, 40 percent. And the CDC estimates that 87 percent of people with HIV know their status, representing a modest gain in testing and awareness.
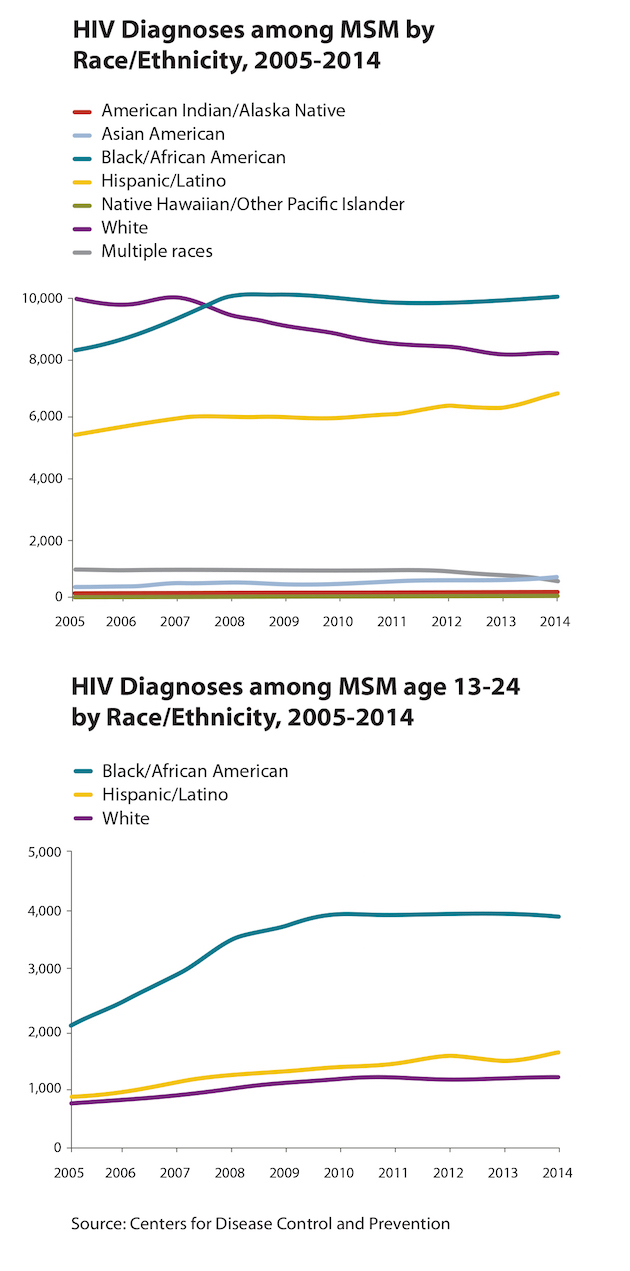
Yet the trend toward steady diagnosis rates masks large disparities among men who have sex with men (MSM), who account for 67 percent of HIV-positive Americans. For black men in this group, already disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS, diagnoses rose 22 percent; for Latino men, they’ve increased almost a quarter, an increase likely attributable to more infections, not better testing, the CDC told The Verge.
The steepest increases in HIV diagnoses have occurred among black and Latino gay youth between the ages of 13 and 24: 5,540 teens received the diagnosis in 2014, a rise of 87 percent since 2005.
Diagnosis stats tell only part of the story: More than two-thirds of transmissions come from people who know that they are HIV positive but are not receiving care. Just 39 percent of people with HIV are being treated for it; only 30 percent have a reduced viral load.
Last Tuesday, CDC director Thomas Frieden published an essay with Jonathan Mermin, the government’s HIV/AIDS prevention chief, warning that the United States may still lose the fight against AIDS. “Hundreds of thousands of people with diagnosed HIV infection are not receiving care,” they wrote. “These people account for most new HIV transmissions in the United States.”
In July, the government released a list of targets for 2020 to measure progress in the fight against HIV/AIDS. They included reducing new diagnoses by at least 25 percent, boosting the percentage of HIV-positive people receiving medical care to 90 percent, and increasing the percentage with suppressed viral loads to 80 percent.
The techniques to fight those battles exist. One promising preventative therapy involves treating uninfected but at-risk people with a combination of anti-HIV drugs known as Truvada. And in May, the CDC halted a study on the effects of early treatment because its benefits were so obvious.
But just because the drugs exist doesn’t mean that people can access them. Last year, CDC researchers highlighted how difficult it can be for some minority communities to receive health care and supportive services for HIV, and they called for better outreach from state and local health departments, community-based organizations, and individual health care providers.
“Faster progress depends on our collective ability to take full advantage of these tools in every community and every region of the country,” wrote the CDC researchers in the latest report. “We need to boldly address stigma, discrimination, and other social, economic, and structural issues that increase vulnerability to HIV and come between people and the care they need.”
This story has been updated.