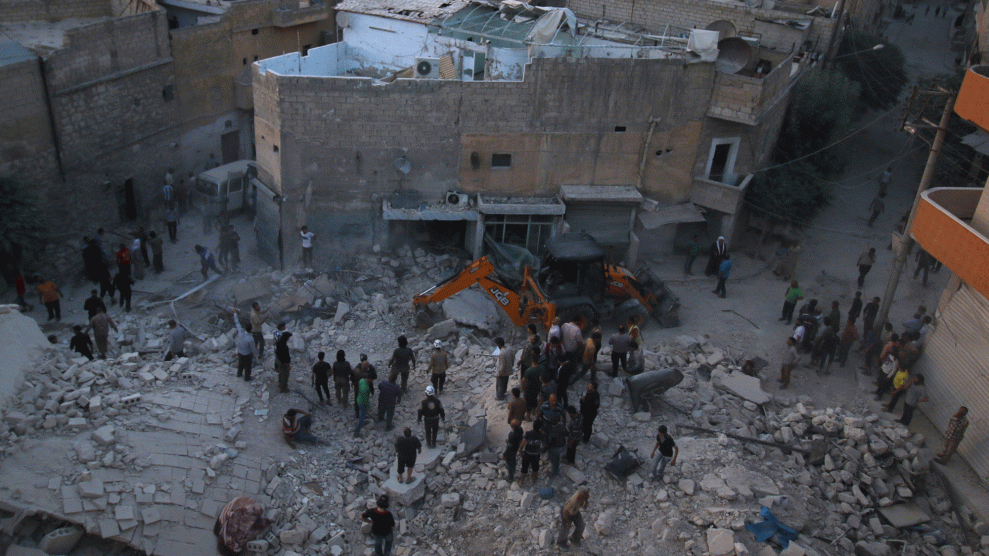People run after airstrikes hit Aleppo, Syria, on August 19.Basem Ayoubi/ImagesLive via ZUMA Wire
On Saturday, just hours after Secretary of State John Kerry and his Russian counterpart Sergei Lavrov announced an imminent cease-fire in Syria, government planes bombed a crowded marketplace killing 61 and wounding 100 more. By weekend’s end, at least 90 people had died in regime airstrikes, including 28 children. Today, President Bashar al-Assad publicly vowed to “recover every inch of Syria from the terrorists” and decried those in the opposition who “were betting on promises from foreign powers, which will result in nothing.”
In other words, the long-awaited Syrian cease-fire appears to be off to a great start.
The agreement, which was announced early Saturday morning in Geneva, officially began at sundown today. It comes after 10 months of failed attempts to reach a political settlement to a conflict that’s killed nearly half a million people and spawned the largest refugee crisis since World War II. While some observers argue that the cease-fire is the best opportunity to bring a pause to the violence, the plan has been greeted mostly with skepticism.
As shoppers queued for Eid (biggest holiday), Regime airstrike hit central market. No words. #Syriaceasefire pic.twitter.com/Pe72iZqofo
— The White Helmets (@SyriaCivilDef) September 10, 2016
If the truce endures for a week and humanitarian aid begins to flow into besieged areas, the United States and Russia say they will put aside their differences over the legitimacy of the Assad regime and work to target two jihadist groups, ISIS and Jabhat al-Nusra, the former Al Qaeda-affiliate that recently rebranded as Jabhat Fateh al-Sham (JFS).
In theory, the cease-fire deal prohibits the Syrian Air Force from flying raids over opposition-held areas, except for those controlled by ISIS or JFS. Kerry called this “the bedrock of the agreement,” labeling the Syrian Air Force the “main driver of civilian casualties.” But as Michael Weiss of The Daily Beast writes, outside of excluding ISIS and JFS, the deal does not clearly define the ideologically mixed groups that make up the Syrian opposition forces.
As part of the agreement, more moderate rebel groups must distance themselves from JFS or risk being targeted. But Syria’s mainstream armed opposition forces, as Charles Lister, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute, puts it, “are extensively ‘marbled’ or ‘coupled’ with JFS forces…This is not a reflection of ideological affinity as much as it is merely a military necessity.” Lister wrote on Saturday that “not a single one has suggested any willingness to withdraw from the frontlines on which JFS is present. To them, doing so means effectively ceding territory to the regime, as they have little faith in a long-term cessation of hostilities holding.”
Teams in Idlib still sifting through rubble after airstrike looking for survivors. RESTRAINT PLEASE #Syriaceasefire pic.twitter.com/CaudbuqYhU
— The White Helmets (@SyriaCivilDef) September 10, 2016
Under the new deal, the Syrian government is only banned from striking areas agreed to by both Russia and the United States, and the Assad regime and Russia are permitted to strike JFS (the group formerly known as Nusra) without prior American consent if it’s in response to “imminent threats.” Weiss asks, “[W]hat is to stop Damascus and Moscow from suddenly finding ‘imminent threats’ everywhere against parties they insist are Nusra or Nusra-affiliated before Washington can concur?”
Bloomberg columnist Eli Lake points out that the Pentagon and the US intelligence community are deeply skeptical about sharing intelligence with the Russians on Syria. Even if the first week’s truce holds, he writes, “is it even desirable for US intelligence officers to be sharing the locations of US-backed rebels in Syria with a Russian Air Force that has been bombing them for nearly a year?”
On Sunday, rebel groups sent a letter to the United States agreeing to “cooperate positively” with the cease-fire. But they added that they have deep concerns “linked to our survival and continuation as a revolution.” Among their top concerns: The agreement neglects many besieged areas outside of Aleppo, lacks guarantees or sanctions against violations, and doesn’t ban Syrian jets from flying for up to nine days following the beginning of the cease-fire. It also called the exclusion of JFS, but not Iranian-backed Shiite militias, a double standard. One American-backed rebel faction has already called the deal a “trap.”
Perhaps to no one’s surprise, reports of alleged cease-fire violations emerged within one hour of its official start on Monday night, as the Assad regime launched artillery strikes on Al-Hara and dropped a barrel bomb on Aleppo.