Jared Bernstein tries to explain today why Thomas Piketty’s Capital in the 21st Century has become such a cultural phenomenon. The answer, he says, is a growing sense that “something is structurally wrong with both the economy and the practice of economics”:
Between financial bubbles and busts, the macro-management seems inept and even once the economy starts growing again, the benefits accrue narrowly to the top. In part, it’s a sense that “the fix is in” when it comes to the distribution of growth.
….Against that backdrop, we get a long, carefully researched tome with literally centuries of data across numerous countries showing a pretty inexorable trend of income and wealth concentration and providing a cogent analysis of  the mechanics behind those dynamics. At the same time, though Piketty clearly knows his economics, he is quick to dismiss a knee-jerk elevation of assumption-based economic analysis that has led so many policy makers astray in recent years. Moreover, he is not a known partisan who can quickly be compartmentalized and thus distractingly plugged into the existing debate that tends to generate more heat than light.
the mechanics behind those dynamics. At the same time, though Piketty clearly knows his economics, he is quick to dismiss a knee-jerk elevation of assumption-based economic analysis that has led so many policy makers astray in recent years. Moreover, he is not a known partisan who can quickly be compartmentalized and thus distractingly plugged into the existing debate that tends to generate more heat than light.
This puzzles me, because it’s precisely what Piketty doesn’t show. Instead, what he shows is this:
- For 1800 years, returns on capital were far higher than growth rates, but wealth concentration didn’t budge over the long term.
- In the 19th century, an era marked by relative peace and the explosive growth of the Industrial Revolution, wealth concentration increased steadily, peaking in the Gilded Age.
- In the 20th century, following the devastation of the Great Depression and World War II, wealth concentration declined.
- Starting around 1980, wealth concentration started increasing again.
Now, Piketty does present good evidence to suggest that the post-1980 trend of rising wealth concentration is likely to continue. With the increasing financialization of the global economy, he believes that returns to capital will stay high; that low inheritance taxes will allow great fortunes to perpetuate themselves; and that sluggish economic growth will limit middle-class earnings gains. This dynamic will take a while to play out fully, but a century from now the relentless forces of r > g will produce a super-rich class with a far, far greater share of global wealth than they have today.
Now, Piketty may be right about this. I think the case he makes is a strong one. Nevertheless, the lesson I took from the book is that wealth concentration is highly variable. It bounces up and down over the centuries, increasing in certain places and eras, and then dissipating via war, famine, dissolute sons, lavish spending, expropriation, dispersion among heirs, disruptive technologies, and so forth. Right now, wealth concentration has been rising for a few decades, and that’s something worth grappling with for all the reasons Piketty lays out.
And yet, I can’t help thinking that on the time scales Piketty writes about, a few decades is a historical blip. There’s simply no “inexorable trend” visible in his data. Instead, there’s a highly speculative projection that the short-term trend of the past 30 years will continue for another century.
It might, but I wish more people would pay attention to just how speculative this is. Perhaps you think that war and expropriation and famine are no longer big threats to concentrated wealth. Perhaps dissolute sons all now have professional money managers and are less likely to squander huge family fortunes. Maybe middle-class wage growth is doomed to stagnate in a world dominated more and more by a highly-educated class managing complex technologies. Maybe disruptive technologies have gotten to the point where they benefit only the 1 percent, shifting wealth from one faction to another but never trickling down to the middle class. (I happen to find this scenario extremely likely, believing as I do that automation is likely to increase returns to capital and depress middle-class wage growth.)
I understand that I’m playing devil’s advocate here, especially since growing income inequality is a topic I write about frequently and I personally find it likely that Piketty is basically right. But I also recognize that his projections—of growth, of returns to capital, and of the persistence of dynastic wealth—are highly speculative. The past 30 years are hardly unique in human history, and previous waves of wealth concentration have not, in fact, lasted forever. I guess I wish that more people would at least acknowledge this. I feel like we should all be spending more time extending and refining Piketty’s results instead of simply assuming that he’s made a slam dunk case for the future of the economy.
 the chart also add some appropriately scholarly cautions:
the chart also add some appropriately scholarly cautions:
 the mechanics behind those dynamics. At the same time, though Piketty clearly knows his economics, he is quick to dismiss a knee-jerk elevation of assumption-based economic analysis that has led so many policy makers astray in recent years. Moreover, he is not a known partisan who can quickly be compartmentalized and thus distractingly plugged into the existing debate that tends to generate more heat than light.
the mechanics behind those dynamics. At the same time, though Piketty clearly knows his economics, he is quick to dismiss a knee-jerk elevation of assumption-based economic analysis that has led so many policy makers astray in recent years. Moreover, he is not a known partisan who can quickly be compartmentalized and thus distractingly plugged into the existing debate that tends to generate more heat than light.
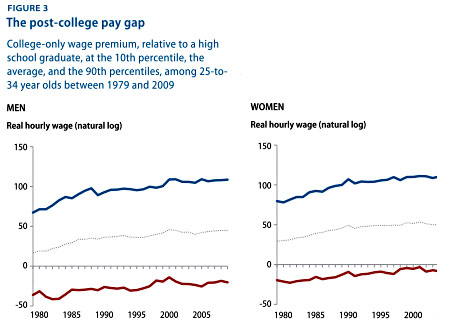 college it is important that most can predictably benefit from the additional education, not just that the average pay of college grads rises.
college it is important that most can predictably benefit from the additional education, not just that the average pay of college grads rises.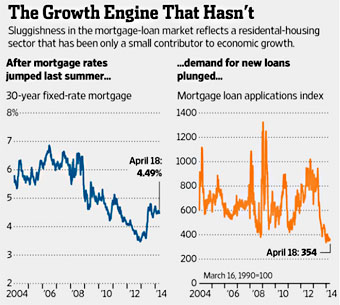 Second, as the Wall Street Journal reports, rising interest rates have
Second, as the Wall Street Journal reports, rising interest rates have 




